Search Results for: chronic disease
Chronic disease
Chronic disease diseases which have one or more of the following characteristics: they are permanent, leave residual... Read More
Myocardium
Myocardium Definition What is the myocardium of the heart? It is the muscular middle layer of the heart that is... Read More
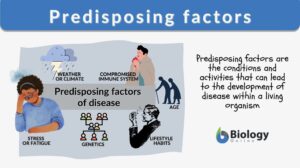
Predisposing factors
All organisms can be born with or develop a disease at any point in their lifetime. When someone is born with a disease, it... Read More
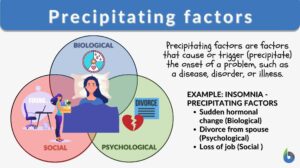
Precipitating factors
Precipitating Factor Definition Precipitating factors are factors that initiate or promote the onset of any illness,... Read More
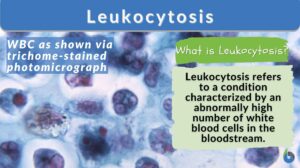
Leukocytosis
What Is Leukocytosis? Leukocytosis is a condition wherein the number of White Blood Cells (WBCs) is increased above the... Read More
Prodromal period
There are five stages (or phases) of a disease. (Hattis, 2020). These stages are (1) Incubation period, (2) Prodromal... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
coronavirus COVID-19
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious coronavirus disease first detected... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use
IV. Actions of Caffeine on Brain Functions and Behavior Having discussed the molecular and neuronal actions of caffeine,... Read More
Residual volume
Residual volume is a term that is most often seen in lung physiology where it is defined as the amount of air remaining in... Read More
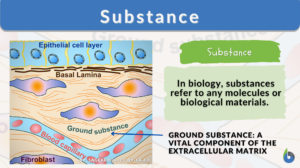
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More
Elephantiasis
Definition noun, plural: elephantiases A disease of the skin characterized by being thick, rough, hard, and fissured, like... Read More
Hypotonic solution
Hypotonic Solution Definition What is a hypotonic solution? It refers to a solution that contains a lower amount of solute... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
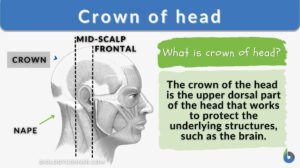
Crown of head
Crown of Head Definition The crown of the head is the upper dorsal part (or area) of the head. Several creatures have... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
Erythropoietin
Definition noun, plural: erythropoietins A glycoprotein hormone that regulates the production of red blood cells in the bone... Read More
Integumentary system
Integumentary System Definition The integumentary system is the outermost layer of the body. The animal body, in... Read More
Dumdum fever
Dumdum fever --> visceral leishmaniasis a chronic disease, occurring in india, Assam, china, the area formerly known as... Read More
Black sickness
Black sickness --> visceral leishmaniasis a chronic disease, occurring in india, Assam, china, the area formerly known as... Read More
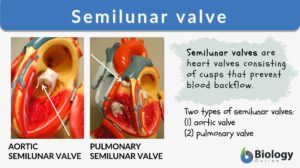
Semilunar valve
The human heart structure consists of heart chambers (2 atria and 2 ventricles) that differ functionally from each other.... Read More
Flax-dressers disease
Flax-dressers disease (Science: disease) chronic obstructive pulmonary disease caused by inhalation of particles of... Read More
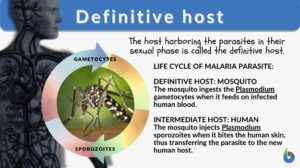
Definitive host
Different Biological Relationships The biological world is interconnected whether we notice it or not. All the life forms... Read More
The Psychobiology of Hysteria
Editorial Hysteria is often regarded as the archetypal psychodynamic illness. Freud carried out much of his early work on... Read More
Adipose tissue
Adipose Tissue Definition Adipose tissue, a specialized variety of connective tissue, is composed of lipid-rich cells known... Read More
Cholesterol
Definition noun A sterol or a modified steroid that is synthesized by animal cells to become an essential component of... Read More